Human Resource Management (HRM) is the backbone of every organization because it focuses on managing people effectively. Many people often ask what is human resources management and the answer is simple: it is all about handling employees from hiring to retirement. Human resources or HR covers everything from recruitment, payroll, and compliance to growth and engagement.
With the rise of technology, companies now use HRMS and HR Management Systems to simplify processes and HRIS to store human resources information in one place. Human resources online platforms have made it easy to access data, track performance, and support employees anywhere.
Introduction to Human Resource Management (HRM)
Human Resource Management (HRM) is an essential part of every business as it deals with people, the most important resource of any organization. When we talk about what is human resources management, it simply means taking care of employees throughout their journey in the company, from recruitment and training to performance, payroll, and retirement. Human resources, or HR, ensures that employees feel supported, motivated, and aligned with business goals.
What is the Meaning of HRM in Layman Terms?
Human Resource Management (HRM) simply means managing people at work. It’s about hiring the right people, giving them proper training, keeping them motivated, paying them fairly, and making sure they follow company rules. In short, HRM is how a company takes care of its employees so that they can perform well and help the business grow.
What is the Official Definition of HRM?
Human resource management is the function within an organization that focuses on the recruitment, management, and direction of the people who work in the organization.
Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM)
Brief History and Evolution of HRM
19th Century
- Pre-Industrial Era (before 18th century):
Work was mostly agricultural or craft-based; there was no formal concept of Human Resource Management. Masters and owners managed workers directly.
- Industrial Revolution (18th–19th century):
Growth of factories created the need for structured worker management. The focus was on hiring labor, maintaining discipline, and keeping wages low.
20th Century
- Early 1900s – Welfare & Personnel Management:
Companies introduced welfare officers and personnel departments to handle worker grievances, safety, and basic training.
- 1920s–1930s – Scientific Management & Human Relations Movement:
Frederick Taylor’s Scientific Management emphasized efficiency and productivity. Later, the Hawthorne Studies showed the importance of motivation, teamwork, and employee satisfaction.
- 1940s–1950s – Personnel Administration Expansion:
After World War II, personnel management grew to include compensation, labor relations, and compliance with labor laws.
- 1960s–1970s – Birth of Human Resource Management (HRM):
The focus shifted from administrative tasks to employee development, motivation, and organizational culture. Training, performance management, and employee engagement became central.
- 1980s–1990s – Strategic HRM:
HR evolved into a strategic partner, aligning workforce planning with business goals. Introduction of HRIS (Human Resources Information Systems) automated many HR functions.
21st Century
- 2000s – Technology & HRMS:
Digital tools, HRMS, and online platforms transformed HR into a data-driven function. Remote access and human resources online systems became common.
- 2010s–Present – Modern HRM:
HR now focuses on employee experience, diversity & inclusion, people analytics, and automation. HR is seen as a business partner shaping strategy, not just managing administration.
Why Human Resource Management is Important?
Human Resource Management is important due to several notable reasons. Let us throw light on few of them.
- Right People for the Right Job
HRM ensures that organizations hire skilled people who fit the role and the company culture. - Training and Growth
Through human resources training, employees develop new skills, stay updated, and perform better. - Motivation and Engagement
HR keeps employees motivated with fair pay, benefits, and recognition, which leads to higher productivity. - Smooth Business Operations
By managing compliance, policies, and workplace relations, HR prevents conflicts and ensures smooth day-to-day functioning. - Strategic Business Partner
Modern HRM uses HRMS and HRIS to provide human resources information and analytics that help leaders make better decisions for growth.
Objectives of Human Resource Management (HRM)
Human Resource Management (HRM) is very important for every company. Its main goals are to improve the HR strategy and help the organization grow. Let us discuss the inevitable objectives of HRM.
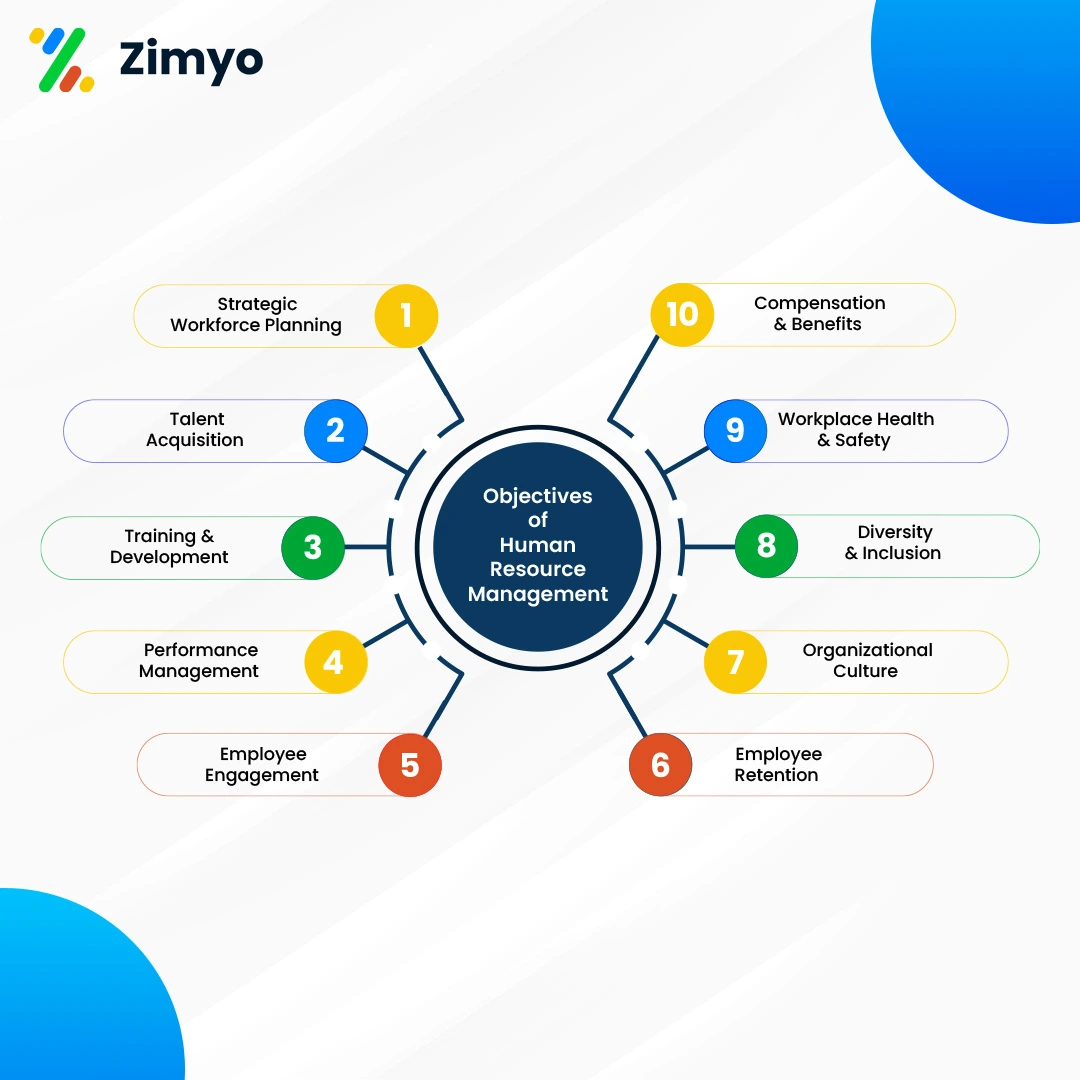
- Strategic Workforce Planning – Aligning the workforce with long-term business goals through careful forecasting and planning.
- Talent Acquisition – Attracting and hiring the right people with the right skills for the right roles.
- Training and Development – Providing employees with opportunities to learn, grow, and improve their skills.
- Performance Management – Monitoring and evaluating employee performance to ensure goals are met.
- Employee Engagement – Keeping employees motivated, satisfied, and connected to the organization.
- Compensation and Benefits – Offering fair pay, incentives, and benefits to reward and retain talent.
- Workplace Health and Safety – Ensuring safe, healthy, and compliant working conditions for all employees.
- Diversity and Inclusion – Promoting equal opportunities and building a culture that values differences.
- Organizational Culture – Creating a positive, collaborative, and value-driven work environment.
- Employee Retention – Reducing turnover by building loyalty and long-term commitment among employees.
Functions of Human Resource Management
The functions of Human Resource Management (HRM) include hiring, training, managing performance, rewarding employees, and ensuring a positive workplace. We jotted down various indispensable functions of HRM.
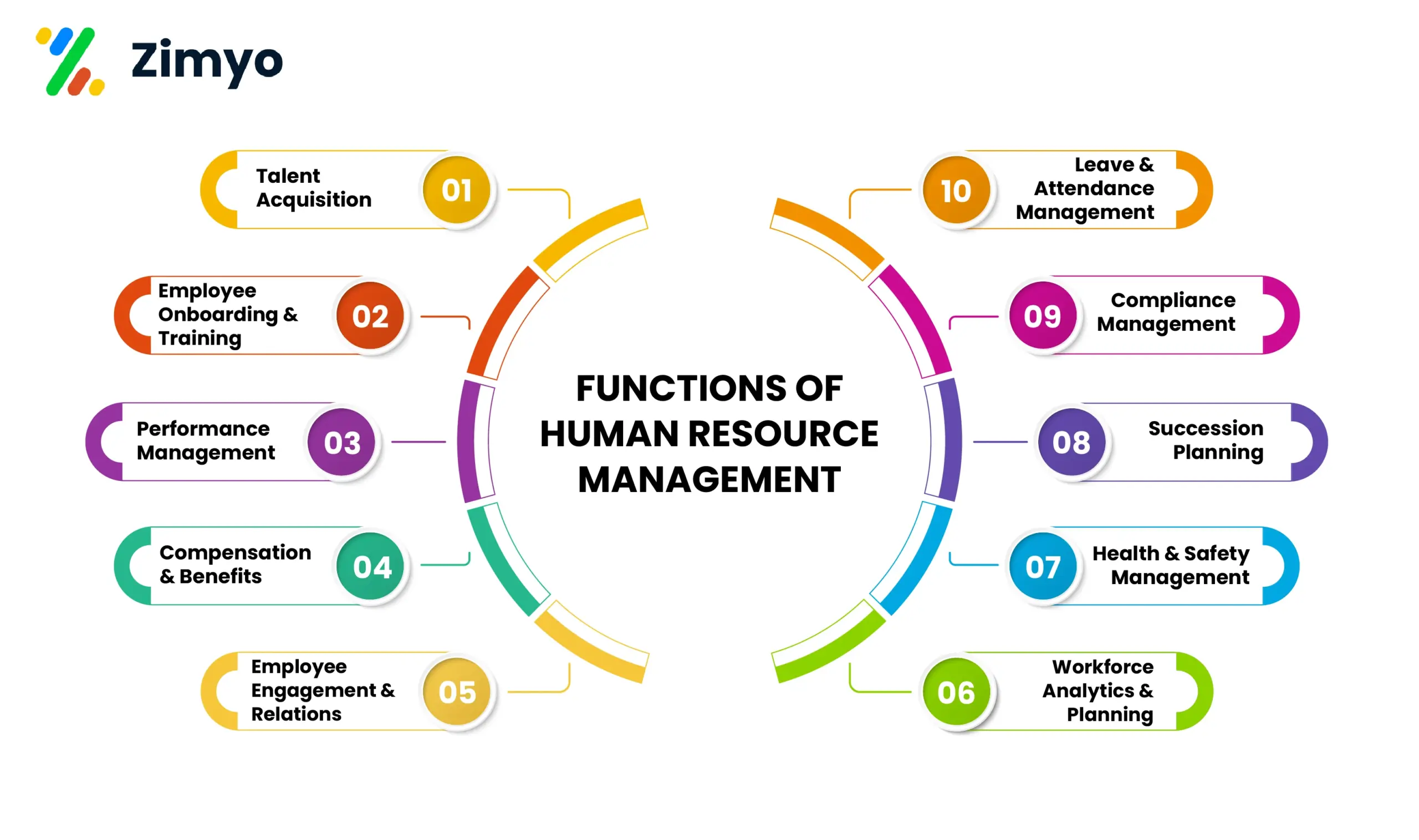
- Talent Acquisition
Finding, attracting, and hiring the right people for the right job through job postings, interviews, and assessments. - Employee Onboarding and Training
Helping new employees settle into the company and providing them with human resources training to build required skills. - Performance Management
Monitoring, reviewing, and improving employee performance using feedback, appraisals, and goal setting. - Compensation and Benefits
Designing fair salary structures, bonuses, incentives, and benefits like insurance and retirement plans to retain employees. - Employee Engagement and Relations
Building strong workplace relationships, motivating employees, and ensuring they feel connected and valued. - Leave and Attendance Management
Tracking employee attendance, managing leave requests, and ensuring work continuity without disruptions. - Compliance Management
Making sure the company follows labor laws, workplace policies, and industry regulations to avoid legal issues. - Succession Planning
Identifying and preparing future leaders within the company to fill key roles when needed. - Health and Safety Management
Creating safe workplaces by implementing safety rules, health programs, and employee wellness initiatives. - Workforce Analytics and Planning
Using HRMS and HRIS to analyze human resources information, predict workforce needs, and plan for the future.
HRM vs HRIS vs HRMS vs HCM
HRM, HRIS, HRMS, and HCM are common terms in human resources management, and while they are closely related, each serves a unique role in managing people and processes.
|
Term |
Full Form |
Focus Area |
Key Features |
Best For |
|
HRM |
Human Resource Management |
Managing people in an organization |
Recruitment, training, performance, compensation, employee relations |
Overall management of human resources |
|
HRIS |
Human Resources Information System |
Data and record keeping |
Employee database, payroll, attendance, compliance tracking |
Storing and managing human resources information |
|
HRMS |
Human Resource Management System |
End-to-end HR automation |
Combines HRIS + advanced tools like onboarding, performance, analytics |
Companies needing digital HR Management Systems |
|
HCM |
Human Capital Management |
Strategic workforce management |
Talent acquisition, succession planning, employee development |
Organizations focusing on people as strategic assets |
Benefits of Implementing HRM in Organizations
The benefits of implementing Human Resource Management (HRM) in organizations include better employee performance, stronger engagement, and smoother HR processes. Let us discuss each of the benefits of HRM.
- Better Hiring Decisions
HRM helps companies attract and select the right candidates, saving time and reducing wrong hires. - Improved Employee Productivity
Through human resources training, performance management, and engagement programs, employees perform at their best. - Higher Employee Satisfaction
Fair compensation, benefits, and recognition make employees feel valued and motivated. - Smooth Compliance
HRM ensures that organizations follow labor laws, workplace safety standards, and ethical practices, avoiding legal risks. - Cost and Time Savings
By using HRMS and HRIS, companies automate routine HR tasks like payroll, leave tracking, and reporting. - Stronger Employee Relations
HRM builds trust and better communication between employees and management. - Strategic Business Growth
HRM aligns workforce planning with organizational goals, making human resources management a partner in long-term success.
Challenges in Human Resource Management
The challenges in Human Resource Management (HRM) arise from changing workplace needs, new technologies, and the constant demand to keep employees engaged and productive.
- Talent Acquisition and Retention
Finding skilled employees and keeping them motivated in a highly competitive job market. - Adapting to Remote and Hybrid Work
Managing productivity, communication, and engagement for employees working from different locations. - Compliance with Labor Laws
Keeping up with changing regulations related to wages, benefits, safety, and workplace equality. - Employee Engagement and Satisfaction
Maintaining morale, reducing stress, and creating a positive work culture. - Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI)
Building inclusive workplaces that respect differences and promote equal opportunities. - Technology Adoption
Implementing and managing HRMS, HRIS, and other HR Management Systems effectively without overwhelming employees. - Skill Gaps and Training Needs
Continuously upskilling employees to match the fast-changing business environment. - Handling Workforce Data and Analytics
Using human resources information wisely for decision-making while ensuring data security and privacy.
Modern Trends in HRM
Modern trends in Human Resource Management (HRM) focus on using technology, improving employee experience, and creating flexible and inclusive workplaces.
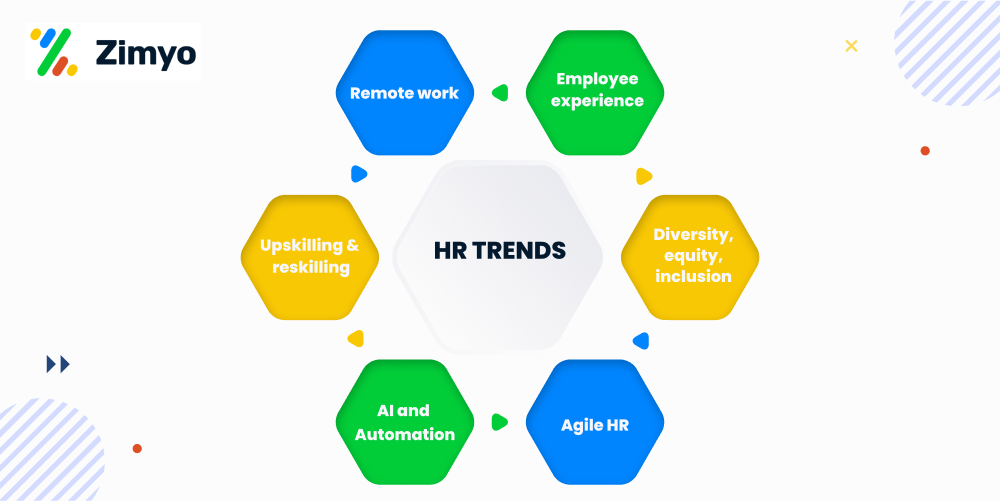
- Artificial Intelligence and Automation
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and automation are transforming HR functions. AI-powered tools like chatbots can now handle routine tasks such as resume screening, scheduling interviews, and answering employee queries. This saves time for HR professionals, allowing them to focus on strategic initiatives. AI also helps in analyzing employee data, spotting patterns, and supporting smarter, data-driven HR decisions. - Remote Work
The shift to remote and hybrid work, accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, has become a long-term trend. While it offers flexibility, it also challenges HR to keep employees engaged, motivated, and productive in virtual environments. HR now plays a vital role in building digital work cultures and maintaining strong communication across teams. - Employee Experience
More organizations are prioritizing employee experience to build loyalty and satisfaction. HR is expected to create positive work environments where employees feel valued and supported. This includes offering growth opportunities, flexible working options, career development programs, and promoting work-life balance. - Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI)
Diversity, equity, and inclusion have become central to HR strategies. HR teams are responsible for creating fair policies, addressing workplace biases, and ensuring equal opportunities for all employees. A strong DEI culture helps organizations foster innovation and improve employee trust. - Agile HR
Agile HR focuses on being flexible and adaptive to changing business needs. It involves breaking silos between departments, encouraging collaboration, and using iterative methods to improve HR processes. This approach helps organizations respond quickly to new challenges and opportunities. - Upskilling and Reskilling
As technology and industries evolve, so do the skills required in the workforce. HR must actively invest in upskilling and reskilling programs to prepare employees for future roles—often supported by AI coaching tools like Marlee, which help guide employees through personalized development paths. This not only boosts employee confidence but also ensures the organization stays competitive.
Best HRM Practices for Businesses
The best HRM practices for businesses help build a strong workforce, improve employee satisfaction, and drive organizational success. Following are some of the Best HRM Practices for Businesses:

- Employee Relations – Building trust and resolving conflicts to maintain a positive workplace environment.
- Performance Management – Setting goals, tracking progress, and improving employee performance.
- Recruitment – Attracting potential candidates to fill job openings.
- Selection – Choosing the most suitable candidate from the pool of applicants.
- Compensation – Providing fair salaries, incentives, and benefits to reward employees.
Future of Human Resource Management
The future of Human Resource Management (HRM) is moving toward technology-driven and people-centric strategies. Human resources will rely more on HRMS, HR Management Systems, and HRIS to manage human resources information, automate routine tasks, and provide real-time insights.
Companies will use human resources online platforms, AI tools, and workforce analytics to improve decision-making. The functions of Human Resource Management will expand beyond hiring and payroll to focus on employee experience, upskilling, and long-term growth.
The benefits of Human Resource Management will become even clearer as HR professionals act as strategic business partners. Human resources training and the guidance of a human resources consultant will also play a bigger role in preparing organizations for future challenges.
In short, the future of human resources management is about combining technology with a human touch to build smarter, more agile workplaces.
Conclusion
Human Resource Management (HRM) is more than just handling employees; it is about building a strong, motivated, and future-ready workforce. From core functions like recruitment, training, and performance management to modern practices using HRMS and HRIS, HR has become a strategic partner in business success.
With the right HR Management Systems, human resources training, and best practices, organizations can unlock the full benefits of Human Resource Management. As the future of human resources management evolves with AI, automation, and employee-centric approaches, companies that invest in HR today will lead with stronger teams tomorrow.




