Most enterprises today do not struggle with HR execution.
Their payroll works on time, attendance data is available to them, and performance cycles are completed. Along with compliance requirements handled in a timely manner. From the outside, HR operations appear stable and under control.
Yet when leadership conversations turn strategic, like about scaling teams, reducing attrition risk, building leadership pipelines, or planning future capabilities. HR insights often feel a little fragmented, delayed, or perhaps overly operational.
This right here is not a failure of effort or intent. But a visibility challenge that emerges as organizations grow.
As enterprises mature, expectations from HR shift quietly but decisively. The question is no longer whether HR processes are running efficiently. The question becomes whether people decisions are actively shaping business outcomes.
This transformative shift marks the beginning of Strategic Human Resource Management.
What is Strategic Human Resource Managment (SHRM)?
Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM) is the practice of aligning HR policies and people management strategies with an organization’s long-term business goals to improve performance and drive sustainable growth.
When You Need More Than Operational Maturity
In early stages of growth, HR success is measured by stability. Systems are put in place, policies are standardized, and processes are designed to support expansion. At this stage, efficiency is the primary goal. But for enterprises, efficiency becomes a given.
Leadership expects HR to answer different questions:
- Which roles are critical to future growth?
- Where are capability gaps emerging before performance declines?
- Which teams are at risk of burnout or attrition?
- How do compensation, performance, and engagement intersect?
These are not operational questions. They are strategic ones. Strategic Human Resource Management does not replace day-to-day HR operations. It builds on them. It assumes that execution is reliable and shifts focus to foresight, alignment, and decision quality.
Strategic HRM is a New Way of Thinking
Strategic HRM is often described through models and long-term plans. In practice, it shows up much more quietly.
It appears in how HR leaders interpret patterns rather than individual data points. It shows up in conversations where workforce insights inform business priorities rather than react to them. This is visible when HR moves from reporting what has happened to anticipating what could happen next.
Operational HR asks:
- Are people present?
- Are processes followed?
- Are issues resolved?
Strategic HR asks:
- Where should the organization invest in talent?
- What workforce risks could slow growth in the next year?
- How do people decisions today affect capability tomorrow?
The difference is not activity but rather in the perspective.
The Importance of Strategic HR Management
Importance of human resource management is that it ensures the workforce is optimized to meet organizational goals. It helps businesses gain a competitive advantage by attracting top talent, promoting innovation, and increasing employee productivity. Through effective human resource strategy, organizations can reduce turnover, enhance engagement, and build a high-performance culture.
Objectives of Human Resource Management
The key objectives of human resource management include:
- Workforce Optimization: Ensuring the right people are in the right roles.
- Employee Satisfaction: Creating a positive work environment to boost morale.
- Compliance & Ethics: Ensuring adherence to labor laws and ethical standards.
- Organizational Growth: Supporting business expansion through strategic HRM.
- Technology Integration: Implementing HR systems for improved efficiency.
Key Components of Human Resource Strategy
1. Talent Acquisition & Retention
Finding and retaining the right employees is crucial for business success. Strategic HRM uses advanced hiring practices, including data-driven recruitment and employer branding, to attract top talent.
2. Workforce Planning
HR strategy includes analyzing workforce trends to plan for future needs. Effective resource management ensures that organizations are prepared for growth and market changes.
4. Employee Development & Training
A well-trained workforce leads to improved performance and job satisfaction. Investing in employee learning programs enhances skillsets and boosts productivity.
5. Performance Management
Strategic HRM involves setting clear performance expectations, conducting regular evaluations, and providing constructive feedback to employees.
6. Compensation & Benefits
Competitive salary structures, bonuses, and benefits improve employee retention and satisfaction, making compensation a key element of human resource management.
How Strategic HRM Contributes to Business Success

Strategic HR management plays a crucial role in:
- Enhancing employee engagement and motivation
- Improving organizational efficiency
- Driving innovation through a skilled workforce
- Strengthening employer branding
- Ensuring compliance with labor laws
Let us gain insights about each of these as to how Strategic HRM contributes to business success.
1. Enhancing Employee Engagement and Motivation
- A well-planned human resource strategy ensures employees feel valued and engaged.
- Performance-based incentives and career development programs boost motivation.
- Employee engagement tools in HRMS and HR software help track satisfaction levels.
2. Improving Organizational Efficiency
- HR systems streamline recruitment, payroll, and compliance, reducing administrative burdens.
- Digital HR solutions, including the best HR software, automate time-consuming tasks.
- Workforce analytics in HRIS helps optimize resource allocation.
3. Driving Innovation Through a Skilled Workforce
- Strategic HRM promotes continuous learning and development.
- Companies using human resource management system tools can identify skill gaps.
- Talent development programs encourage innovation and adaptability.
4. Strengthening Employer Branding
- HR strategy enhances workplace culture, making companies more attractive to job seekers.
- Positive work environments and employee advocacy improve brand reputation.
- Human resources services such as recruitment marketing build a strong employer identity.
5. Ensuring Compliance with Labor Laws
- HR systems ensure adherence to employment regulations and ethical standards.
- Legal compliance modules in HRMS and best HRIS mitigates risks.
- Human resources companies provide specialized compliance solutions to reduce legal exposure.
The Role of HR Systems in Strategic HRM
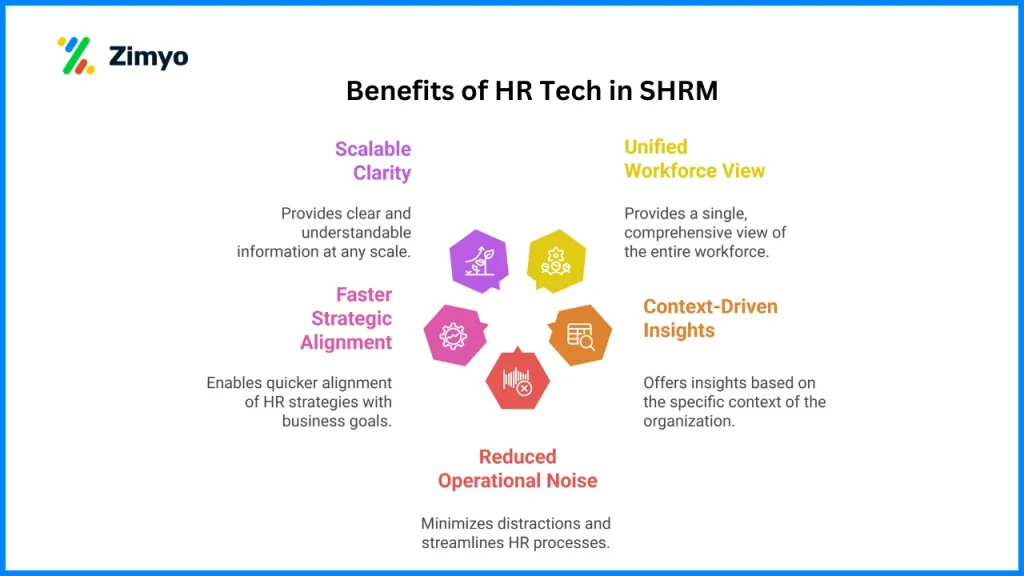
Enterprises do not gauge HR systems by how many processes they automate. But instead, how clearly they enable organizations to see their workforce.
Hence, Zimyo HRMS operates not as a layer of technology added to HR, but as the underlying system with a profound capability to connect people, data, and decisions.
Strategic HRM depends on context. Therefore, decisions around talent, performance, compensation, and workforce planning can’t be made in isolation. And right here, Zimyo brings these elements together, allowing HR leaders to move beyond fragmented reporting toward a unified understanding of their organization.
So, instead of asking HR teams to manually reconcile attendance, payroll, performance, and engagement data, Zimyo provides continuity across the employee lifecycle. This continuity matters. It reduces interpretational gaps, shortens decision cycles, and allows leadership conversations to focus on implications rather than inputs.
In strategic planning discussions, Zimyo enables HR to present insights, and not just numbers. Workforce trends, cost implications, role criticality, and performance patterns all can be viewed together, creating a more accurate picture of organizational readiness. As a result, HR’s role shifts from explaining past outcomes to informing future direction.
Perhaps most importantly, Zimyo supports consistency at scale. As enterprises grow across teams, locations, and business units, maintaining alignment becomes increasingly complex. A centralized HR system ensures that strategy is supported by the same version of truth across the organization, enabling confident, timely people decisions.
In this sense, Zimyo does not “support” Strategic HRM; it sustains it. By providing clarity, structure, and insight, it allows HR leaders to operate at a strategic altitude where foresight matters more than firefighting.
HR Technology plays a vital role in modern HR strategy by automating processes, reducing administrative workload, and improving decision-making.
Challenges in Strategic HRM and How to Overcome Them

Challenges | Solutions |
Resistance to Change | Provide training, communicate benefits, and involve employees. |
Data Security Risks | Implement cybersecurity measures and use encrypted HR software. |
Talent Shortages | Strengthen employer branding and offer competitive salaries. |
Compliance Issues | Stay updated on labor laws and use automated compliance tools. |
Integration of HR Technology | Choose user-friendly HR systems and offer technical support. |
Employee Engagement Challenges | Promote a positive culture and recognize employee efforts. |
Workforce Diversity Management | Promote inclusion and implement unbiased hiring practices. |
Aligning HR Strategy with Business Goals | Conduct regular strategy reviews and use HR analytics. |
Conclusion
Strategic Human Resource Management combined with HR technology is essential for business growth and sustainability. By integrating HR strategy, HR systems, and employee engagement, HRs can build a strong workforce that drives success. Investing in HR software, companies can further align HR functions, making it easier to achieve long-term goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the strategic human resource management?
Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM) is the long-term approach to managing people in a way that aligns HR practices with an organization’s business goals to improve performance, productivity, and growth.
What is the main purpose of SHRM?
The main purpose of SHRM is to ensure that human capital supports business strategy by improving workforce planning, employee performance, leadership development, and organizational competitiveness.
What is an example of SHRM?
An example of SHRM is aligning talent hiring, training, and performance management with future business expansion plans to build the right skills before growth occurs.
What are the 5 P’s of Strategic HRM?
The 5 P’s of Strategic HRM are Purpose, Principles, Processes, People, and Performance, which together help align HR strategy with overall business objectives.







