In the modern workplace, one of the most effective ways to increase performance output and job satisfaction is through the use of incentives. Whether you’re an employee looking to understand your paycheck better, or an employer designing a rewards program, knowing how incentives work is essential.
In this guide, we’ll explore what an incentive is, its types, why it matters, and how it fits into your salary structure or workplace culture.

What is Incentive in Job?
An incentive is a reward or benefit given to employees to encourage and recognize good performance, loyalty, and productivity. It can be in the form of money, recognition, extra time off, or even career advancement opportunities. It act as motivational tools that push employees to achieve more and stay committed to their roles.
To define incentive in simple terms:
An employee incentive is anything that motivates a person to take a specific action or behave in a certain way, especially in a professional or business setting.
In the workplace, it helps bridge the gap between company goals and employee performance.
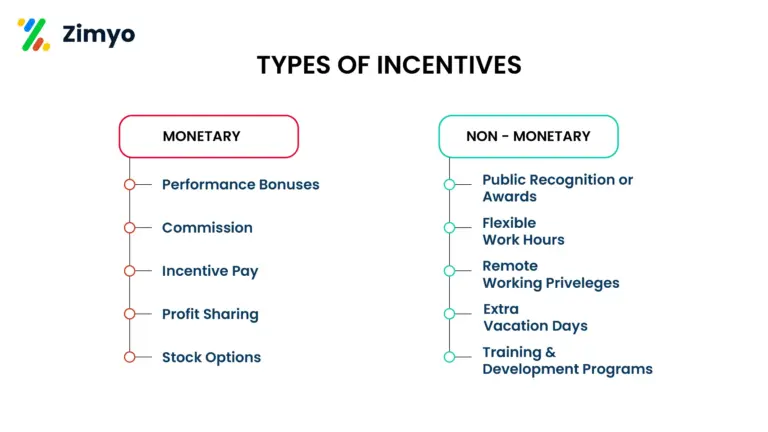
Types of Incentives: Monetary and Non-Monetary
Understanding the types of rewards helps employers design effective incentive schemes that match different roles and preferences.
1. Monetary Incentive
This is the most common type and includes:
- Performance bonuses
- Incentive pay
- Profit-sharing
- Stock options
2. Non-Monetary Incentive
These are non-cash rewards that still provide value, such as:
- Public recognition or awards
- Flexible work hours
- Remote working privileges
- Extra vacation days
- Training and development programs
Incentive in Salary: How Does It Work?
Incentive in salary refers to the additional earnings that employees receive apart from their fixed pay. This bonus is often tied to:
- Individual performance
- Team performance
- Company profits
- Sales targets
- Project completion
For example, a salesperson might receive an incentive pay for exceeding monthly sales goals. This additional income is commonly known as incentive pay.
Popular Incentive Schemes in Companies
An incentive scheme is a structured plan that defines how and when they are given. Some common types include:
- Sales Incentive Plans: Rewarding top sales performers.
- Employee of the Month Programs: Recognizing outstanding work.
- Referral Bonuses: Incentives for bringing in new talent.
- Annual Performance Bonuses: Linked to overall evaluation results.
These schemes are tailored to boost morale, increase retention, and drive productivity.
Explore Our Blog on Employee Referral Program.
Examples in Real Workplaces
Here are some employee incentive examples that show how companies use them effectively:
Company Scenarios | Incentive Used |
Sales rep exceeds target | 10% commission as incentive pay |
Employee finishes project early | Extra paid day off |
Developer completes skill certification | One-time bonus and course reimbursement |
Team meets quarterly goals | Team lunch or outing |
Why Incentives Matter in the Corporate World
Rewards are not just about money. They play a big role in shaping work culture and driving business success. Here’s a quick peak to why they matter:
- Boost Employee Motivation
- Improve Performance and Productivity
- Encourage Healthy Competition
- Reduce Employee Turnover
- Align Personal Goals with Business Objectives
Tips for Creating Effective Incentive Programs
Whether you’re a startup or a large corporation, designing the right incentive scheme requires planning. Here are a few tips:
- Set clear, measurable goals.
- Keep it fair and transparent.
- Personalize rewards based on roles.
- Offer both monetary and non-monetary incentives.
- Review and update regularly based on feedback.
Pitfall to Avoid
In an organization, depending on the type of incentive, the team may or may not work. For example, if you provide individual employee incentives, that will destroy teamwork and collaboration, and everyone will start working individually.
Wrong incentivization (misjudging a wrong behavior) might destroy the positivity and performance of the organization
Conclusion
An incentive is more than just a paycheck booster—it’s a tool that can transform workplace dynamics. By understanding the incentive meaning, its role in salary structures, and the difference between monetary and non-monetary incentives, both employers and employees can work toward shared success.
Whether you’re designing an incentive scheme or trying to understand what incentive in job means for you, remember: when used right, incentives create a win-win for everyone.
FAQs:
What is incentive pay?
Incentive pay is extra compensation given to employees for achieving specific goals or performance targets.
What are some non-monetary incentive examples?
Examples include flexible work schedules, employee recognition, and opportunities for career growth.
Can incentives be part of salary?
Yes, incentive in salary is a common practice, especially in sales, IT, and finance roles.



