Introduction to Egypt Labour Law
Egypt, as the third-largest populace in the world and Africa’s second-largest city, is hub for remote investment. Egyptian labor and company laws combine cutting edge practices with Islamic Sharia law. Further, changes focus on improving transparency, productivity, and cultivating investor certainty. Initiatives like “Egypt Vision 2030” and the “New Investment Law” reflect the country’s commitment to many initiatives.
Furthermore, Egypt’s new Labour Law No. 14 of 2025, effective from September 1st, 2025, will replace the old Law No. 12 of 2003. Thus, HR teams must prioritize legal compliance as the new framework introduces significant changes in maternity leave, wage structures, working hours, and employee benefits.
Egypt Labour Law Regulations
The essential legislation governing labour relations in Egypt is Labour Law 12 of 2003, as amended by Law 180 of 2008. This law diagrams the system for interactions between managers and employees inside Egypt’s private sector.
Additionally, Egypt’s Labor Law outlines essential work conditions, including working hours, rest periods, overtime compensation, and other aspects of the working environment. Also, Social Security Law 79/1975 and the Civil Law Code primarily regulate employee protections and benefits.
Developments in Egypt Labour Law
The Egypt Labour Law includes significant provisions regarding present trends in employment, prioritizing the safety and protection of employees’ rights. These provisions include the following:
- Employment Contracts
- Leave Policies
- Working Hours and Rest Periods
- Wages and Compensation
- Health and Safety Regulations
- Dispute Resolution and Arbitration
- Termination and Severance Benefits
- Employee Rights in Specialized Sectors
1. Employment Contracts in Egypt Labour Law
The Egypt Labor Law establishes the employment contract as the backbone of its framework, legally documenting the terms that define the working relationship between an employer and an employee. In addition, the law requires all contracts to be in writing and include all necessary requirements. Therefore, employers and employees can now negotiate more flexible arrangements.
Probation in Egypt
Probation in Egypt limits to the 3 months.
• Permanent Contracts
Permanent contract is the most common type that offers the greatest employee security. Generally, it alludes to a long-term and renewable contract where there’s no specific end date.
• Fixed-Term Contracts
Further, these are contracts that exist for specific jobs, projects, or time ranges. Moreover, Fixed-term contracts gets at the end of the contract, but when they last for more than two years, counts permanent.
• Part-Time Contracts
Businesses such as retailers, hospitality, and education are accepting the growing need for part-time work. Moreover, part-time workers receive proportional benefits on an hour-for-hour basis.
Thus, an employee cannot do more than one job at a time unless the contract states otherwise, according to the Egypt labor law.
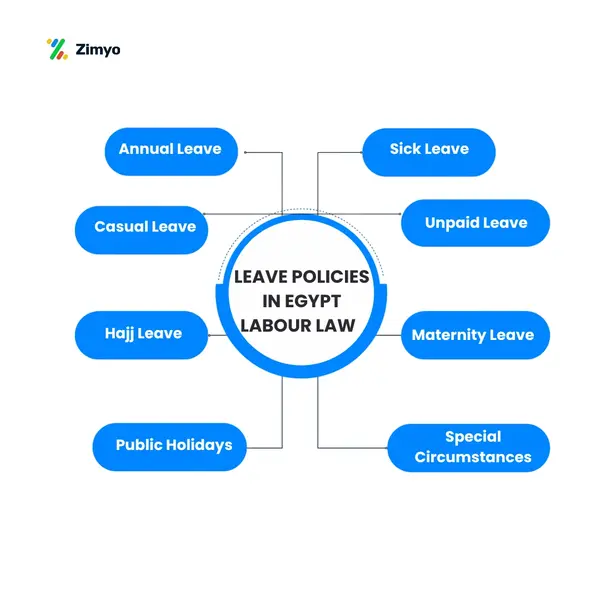
2. Leave Policies under Egypt Labour Law
• Annual Leave
Additionally, those who have completed a full year of work with the same employer gets 21 days of paid annual take-off. Moreover, within the fifth year of employment, the privilege will expand to 30 days. Further, Take-off can get forward for a period not surpassing two a long time if the employee is unable to take leave in Egypt as per the calendar year.
• Sick Leave
Employees who drop sick and cannot work gets 1800 days of paid wiped out leave per year as per Egypt labor law. In any case, the pay structure is as follows:
- First 15 days: Full pay
- Next 30 days: Half pay
- Following 45 days: Unpaid
• Casual leave
According to Article 51 of the Labor Law, employees can only take up to six days of leave for non-essential reasons each year. Each day of leave must be no more than two working days.
• Maternity Leave
Female employees get 90 days full‑pay + 1 hr/day reduction after 6th month of pregnancy maternity leave. Moreover, the women cannot be dismissed or taken any adverse action against them during their maternity leave.
• Public Holidays
- The public holidays in Egypt have certain law that combines with work conditions.
- Since Islamic occasions are according to on the lunar calendar, their dates alter each year.
- Employees who work on national holidays can get 300 times their standard daily salary.
• Additional Types of Leave
- Hajj Leave (Pilgrimage Leave): Employees makes to a one-time fully paid leave to perform the Hajj pilgrimage during their employment.
- Leave for Special Circumstances: Also, employees may receive short-term paid leave for specific life events, such as marriage, exams, or the death of immediate family members. So, the exact terms may vary based on employment contracts or company policies.
- Unpaid Leave: Although not legally mandated, employers may offer unpaid leave for extended personal reasons, provided employer approves it.
3. Working Hours and Rest Periods in Egypt Labour Law
• Standard Working Hours
The law establishes that employees are to work no more than 48 hours a week, typically divided into six working days of 8 hours each. In any case, certain industries or sectors may negotiate reduced working hours in line with business prerequisites.
• Overtime
Those employees who work more than the standard 48 hours gets to overtime minutes’ pay. Employers generally compensate overtime at a rate of 1.5 times the employee’s hourly wage.Thus, for work done at the end of the week or public holidays, employees must get compensation at twice their normal hourly rate as per egypt labor law.
• Rest periods
Employees gets at least 30 minutes of break in every 6 consecutive hours of work. Also, employees might also get satisfactory rest days whereby they get a paid day off each week.
• Night Work
Those who work at midnight, usually from 10 PM to 6 AM, get a few additional recompenses. Thus, night work overtime as a rule pulls in 1.5 times the basic rate per hour.
4. Wages and Compensation
• Salary Payments
Salary must be paid straightforwardly to the employee in Egyptian pounds as egypt labor law or any other money agreed upon in the work contract. Further, the payment should get routinely, ideally monthly, and through coordinate bank transfer or any other method agreed upon.
• Minimum Wage
The Egyptian government has presented 7,000 EGP minimum wage. Further, these suggestions are frequently reviewed to guarantee that employees makes in line with the inflation rate and cost of living.
Salary disbursement in a few clicks
5. Health and Safety Regulations
The Egypt Labor Law gives for workers’ protection from potential workplace risks. Moreover, the bosses gets appoint by the law to make a secure working environment and take all reasonable steps to avoid accidents and injuries.
• Workplace Safety
Here, managers ensure that all equipment, machinery, and tools meet security standards. Additionally, they should implement additional safety measures, such as providing individual protective equipment and regular safety training, according to the Egyptian Labour Law for high-risk industries, such as construction or fabrication.
• Medical Care
In any dangerous trade, the employers shall offer employees health services. Additionally, workers’ compensation insurance must be made to their workers, thus protecting any employees’ medical charges arising from workplace injury.
• Emergency Protocols
There must be emergency protocols established by the employers. Also, the protocols must be regarding fire safety and evacuation procedures. Furthermore, the employees should educate themselves about these emergency procedures.
6. Dispute Resolution in Egypt Labour Law
Disputes between employers and employees are inescapable, and the Egypt Labor Law gives a system for settling such conflicts. Further, the law emphasizes the importance of intervention and arbitration to guarantee fair treatment for all parties included.
- Complaints relating to unpaid wages, wrongful termination, or work-related badgering should get register with the Ministry of Manpower and Immigration (MOMI). The MOMI might examine the complaint and try to solve the case by way of mediation.
- Mediation and Arbitration: The MOMI will mediate between the employee and boss in case of a conflict, aiming to amicably settle the circumstance. Though, if mediation fails to resolve the issue, the case moves forward for assertion or to the labor court.
- Labor Courts: Labor courts will analyze cases that cannot be resolved through mediation. Additonally, they will hear both parties and issue a binding judgment. Employees can appeal to labor courts for justice if they feel unfairly dismissed or have unresolved issues with compensation.
7. Termination and Severance Benefits
Employers and employees are protected by provisions that ensure termination of work. Thus, managers must follow proper procedures outlined by Egyptian labour law when rejecting a worker to ensure a fair and legal process.
• Notice Period
Employers must give employees appropriate notice when terminating their employment. Thus, the length of the notice period depends on the terms of the business contract but generally ranges from 30 to 90 days.
Moreover, reduced pay includes the minimum salary of 2 months of per year employment.
• Severance Pay
The company will provide severance pay to employees who are subject to summary dismissal or retirement after working for more than one year, based on their length of service. Employees will receive one-twelfth of one month’s compensation per year of service.
• Unfair dismissal
Where a representative feels they are unfairly dismissed, they can report the issue to the Ministry of Manpower. Lastly, if the specialist feels that the dismissal was unjustified, they has the right to compensation, counting reinstatement or top-up severance pay.
Stay compliant, stay informed
Work Permits and VISA
In Egypt, foreign nationals must get the appropriate work permits and visas to lawfully work in the nation. These permits and visas are given by Egypt labor laws. Also it includes Labor Law No. 12 of 2003 and the Foreigners Employment Law (Law No. 72 of 2017). Here’s an outline of the types of work licenses and visas:
- Work Permit: Foreigners employed in Egypt must get a work permit from the Ministry of Manpower and Immigration. However, the boss provides documentation proving the position cannot be filled by a nearby Egyptian specialist. Also, a work permit is typically issued for a period of up to 10 years and is renewable, but only a limited number of grants are given each year, depending on the sector and the company’s needs.
- Employment Visa: A foreign worker requires a work visa to work in Egypt. This visa is ordinarily substantial for up to one year and must get renews. Also, the method involves submitting a visa application through the Egyptian office or embassy within the worker’s home country. In addition, to apply, the manager must give a contract and proof of a work permit approval.
- Temporary Work Permit: Foreign nationals coming to Egypt for a short-term assignment or project must obtain a permit. Typically, employers must provide the scope of work and essential documentation to obtain this permit, which typically allows for a few months to complete a particular task or project.
- Freelancer Permit: Foreign nationals offering services in Egypt must apply for a freelancer permit. This permit allows them to work on a contract basis with multiple clients. Thus, proof of business registration and contracts with clients is required to obtain the permit.
- Investor Permit: Foreign investors who wish to operate their businesses in Egypt must apply for an investor permit, which allows them to work in their claim company. Therefore, this permit requires proof of the investment and company registration, along with other documentation.
- Specialized Worker Permit: The Ministry of Manpower grants permits to foreign nationals with specialized skills to work in specific areas or industries. Thus, employers must demonstrate that the position requires skills unavailable locally and provide the necessary documentation.
- Part-time Work Permit: Foreign workers on part-time contracts must apply for this permit, which allows them to work fewer hours than full-time employees. Accordingly, the manager must provide details about the working hours and job duties.
- Student Work Permit: Egyptian students on student visas can apply for a student work permit to work part-time in Egypt, as allowed by labour law. Furthermore, this permit limits the number of hours students can work and the types of jobs they can take.
- Mission Visa: Foreign nationals on temporary assignments or short-term missions in Egypt must obtain a mission visa. Thus, this visa is for ventures and has a limited term based on the assignment.
- Compliance and Documentation: Employers must comply with labor market controls. Moreover, it must illustrate that there are no qualified Egyptian candidates available for the position before contracting a foreign national. Also, all remote representatives are required to supply valid employment contracts, proof of qualifications, and sometimes experience a restorative examination. Lastly, the Ministry of Manpower is dependable for issuing work permits and ensuring compliance with local Egypt labor laws.
Establishing a legal entity in Egypt
Setting up a legal entity in Egypt has traditionally been challenging, with the nation ranked 114th all-inclusive in terms of ease of doing trade. However, later reforms in Egypt labour law have made the method more accessible.
The GAFI directs company registration, which is now available online. Changes have eliminated or reduced capital requirements, especially for small businesses, and the presentation of “One-Stop Shops” has streamlined the process. Moreover, the government is effectively working to draw in foreign investment by advertising benefits such as facilitating the repatriation of profits.
Different types of visas, including business, work, and residency, have diverse eligibility criteria, whereas some businesses have investment restrictions.
Further, common company structures in Egypt incorporate One-Person Companies, Joint-Stock Companies, and Restricted Risk Companies.
Employer Compliance Checklist: Egypt Labour Law
Additionally, ensure your organization is aligned with the latest labor regulations in Egypt. Use this checklist to stay compliant:
Employment Contracts
- All employees signed written contracts.
- The contracts clearly outline job roles, compensation, working hours, and benefits.
- Probation periods do not exceed 3 months.
Working Hours & Rest
- Employees work no more than 48 hours per week.
- They are given a paid weekly rest day, typically on Friday.
- Breaks of at least 30 minutes are provided after six consecutive hours of work.
Leave Entitlements
- Employees receive at least 21 days of paid annual leave (30 days after 5 years).
- Maternity leave is granted for 90 days with full/half pay as applicable.
- Sick leave policy is implemented in line with statutory pay brackets.
- Casual and special leave provisions are clearly communicated.
Wages & Compensation
- Employees receive monthly salaries through traceable methods, such as bank transfers.
- Overtime pay is calculated and disbursed at a rate of (1.5x or 2x).
- Pay structures adhere to Egypt’s sector-specific minimum wage guidelines.
Health, Safety & Insurance
- Workplaces are equipped with safety gear and protocols.
- Emergency procedures and first-aid kits are in place.
- Workers’ compensation insurance is active for occupational injuries.
Termination & Exit
- Termination processes follow due notice (30–90 days based on contract).
- Severance and redundancy pay are calculated accurately.
- Employees have access to grievance and dispute redressal mechanisms.
Foreign Workers & Permits
- All foreign employees have valid work permits and visas.
- Documentation is filed with the Ministry of Manpower as required.
- You’ve verified that no qualified Egyptian national was available before hiring a foreign national
Conclusion
Additionally, the Egypt Labor Law promotes both better rights and protection for employees, making the work environment fair and balanced.Thus, Employers and employees have a clear framework for payroll with employment contracts, working hours, wages, health and safety, and dispute resolution.
However, you should be keenly aware of Egypt’s labor laws before establishing any expansion. Ensure proper understanding and effective implementation by legal standards.
Thus, this HR software empowers organizations in Egypt to oversee employee contracts and ensure compliance with labour laws. Moreover, it helps businesses develop a work environment that contributes positively to the nation’s economy.
Elevate your overall employee experience
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The chief law is the Labor Law No. 12 of 2003 (modified by Law 180 of 2008) of Egypt, Social Security Law 79/1975 and the Civil Law Code.
Yes. The updates of 2026 strengthen the preferable contracts, explain the termination benefits further, and support worker protections in conformity with international labour standards.
The usual working time is also limited to 48 hours per week and is usually spread on 6 days (8 hours a day). All overtime should be payable.
The women employees will have a right of taking 90 days paid maternity leave with 45days on full pay and the rest partially paid.
What People Think About Zimyo